Disease Prediction and Big Data Analysis System: A Machine Learning-Based Multi-Disease Risk Assessment with Interpretability Analysis
Keywords:
Machine learning, Disease prediction, Multi-disease analysis, SHAP interpretability, Risk assessment, Chronic diseasesAbstract
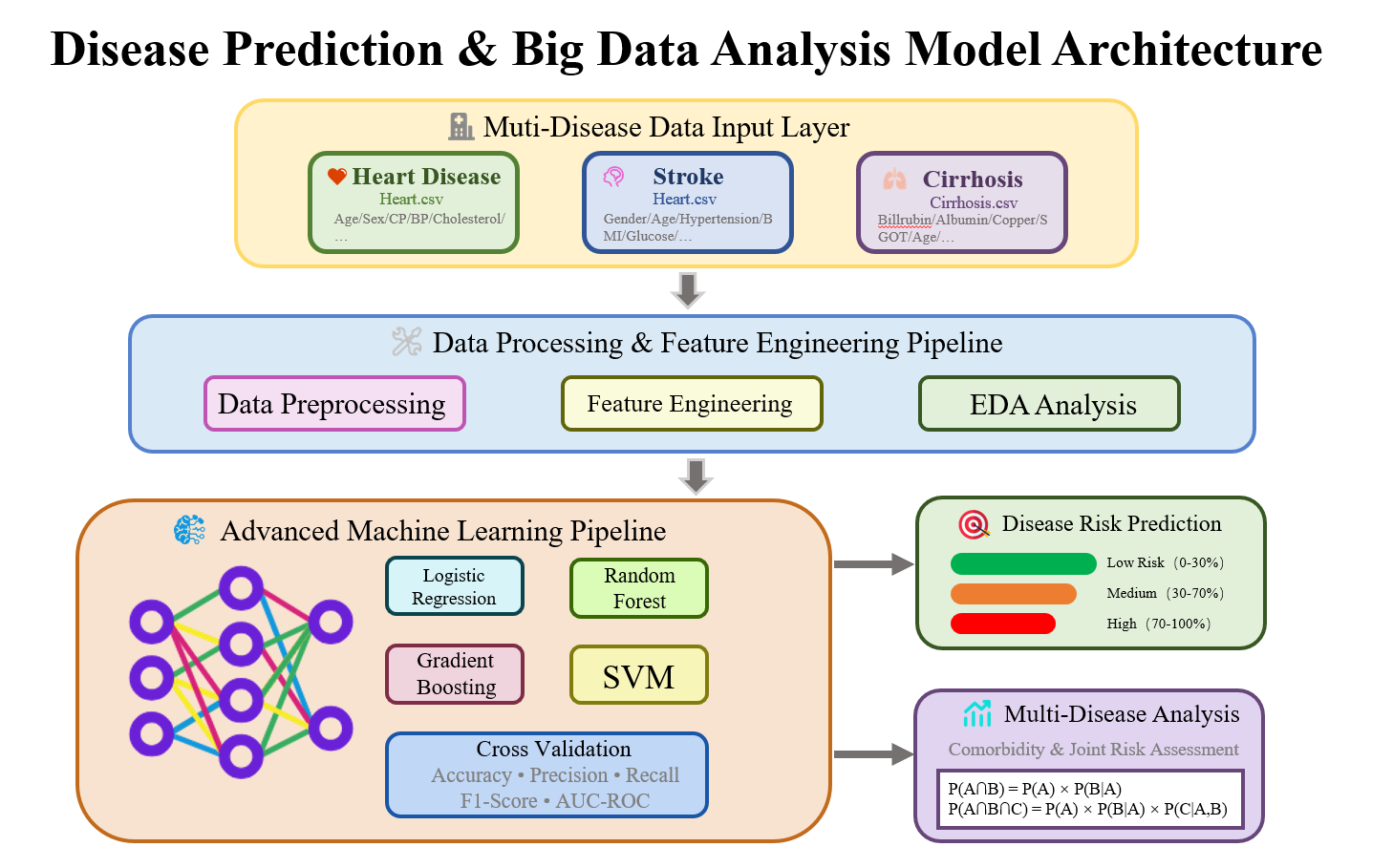
Chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cirrhosis pose significant global health challenges, necessitating advanced prediction and risk assessment systems. Traditional diagnostic methods suffer from limitations including subjectivity, limited accuracy, and inability to process complex multidimensional data effectively. This study presents a comprehensive machine learning-based disease prediction and big data analysis system that integrates multiple algorithms with interpretability analysis for accurate multi-disease risk assessment. The system processes three datasets containing 6,451 patient records across heart disease (920 patients), stroke (5,111 patients), and cirrhosis (420 patients) using four machine learning algorithms: Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, and Support Vector Machine. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) methodology provides model interpretability, while multi-disease association analysis reveals comorbidity patterns. Results demonstrate superior performance with Gradient Boosting achieving AUC scores of 0.942 (heart disease), 0.867 (stroke), and 0.891 (cirrhosis). Multi-disease analysis reveals 23.1% co-occurrence rate between heart disease and cirrhosis, with 15.2% of patients classified as high-risk for multiple diseases. The system generates WHO-compliant reports and personalized risk assessments, providing a comprehensive framework for precision medicine and evidence-based prevention strategies.
References
World Health Organization, "Cardiovascular diseases," WHO Health Topics, Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases
C. Bushnell et al., "2024 Guideline for the Primary Prevention of Stroke: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association," Stroke, vol. 55, no. 12, pp. e344-e424, 2024.
D. E. Gülcicegi, T. Goeser, and P. Kasper, "Prognostic assessment of liver cirrhosis and its complications: current concepts and future perspectives," Front Med, vol. 10, pp. 1268102, 2023.
Naser, M. A. et al., "A Review of Machine Learning's Role in Cardiovascular Disease Prediction: Recent Advances and Future Challenges," Algorithms, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 78, 2024.
K. Shameer et al., "Machine learning prediction in cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis," Scientific Reports, vol. 10, pp. 16057, 2020.
M. M. Alsaleh et al., "Prediction of disease comorbidity using explainable artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques: A systematic review," International Journal of Medical Informatics, vol. 175, pp. 105088, 2023.
S. Uddin et al., "Comorbidity and multimorbidity prediction of major chronic diseases using machine learning and network analytics," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 201, pp. 117021, 2022.
C. Molnar, "Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black Box Models Explainable," 2nd edition, 2023.
World Health Organization, "Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013-2020," Geneva: WHO Press, 2013.
R. Islam, A. Sultana, and M. R. Islam, "A comprehensive review for chronic disease prediction using machine learning algorithms," Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology, vol. 11, pp. 27, 2024.
S. M. Lundberg and S. I. Lee, "A unified approach to interpreting model predictions," in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30, pp. 4765-4774, 2017.
Ogunpola, Adedayo, et al., "Machine Learning-Based Predictive Models for Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases," Diagnostics, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 144, 2024.
A. Sorayaie Azar et al., "Predicting stroke severity of patients using interpretable machine learning algorithms," European Journal of Medical Research, vol. 29, pp. 547, 2024.
P. Chakraborty et al., "Predicting stroke occurrences: a stacked machine learning approach with feature selection and data preprocessing," BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 25, pp. 329, 2024.
Liu, Tianyi, et al., "Machine learning based prediction models for cardiovascular disease risk using electronic health records data: systematic review and meta-analysis," European Heart Journal Digital Health, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 7-18, 2024.
H. Lu and S. Uddin, "Comorbidity and multimorbidity prediction of major chronic diseases using machine learning and network analytics," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 201, pp. 117021, 2022.