Evolution of Carbon Emissions and GDP Decoupling in Vietnam's Electricity Sector
Keywords:
Carbon Emissions, Power Sector, Decoupling Analysis, VietnamAbstract
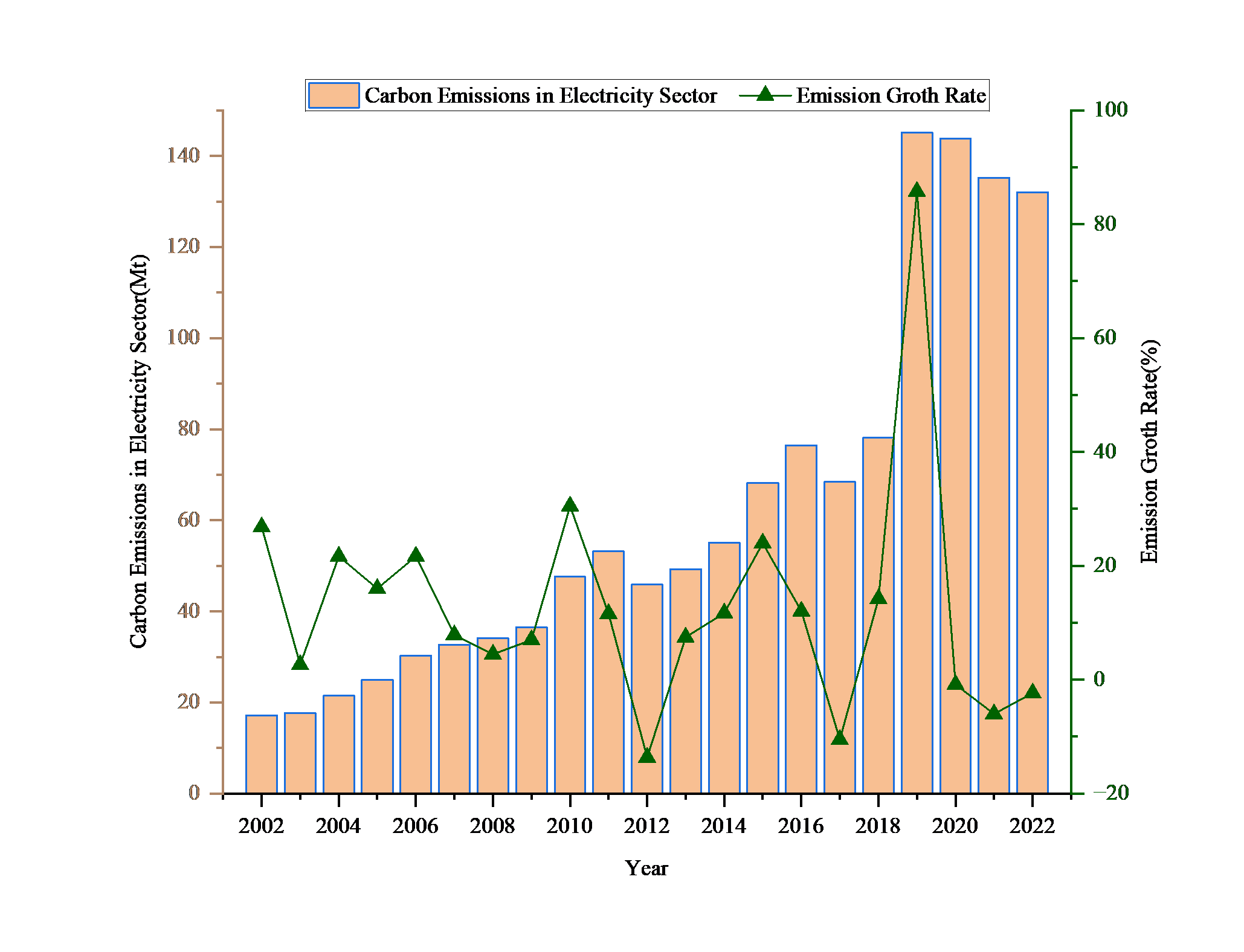
This study examines the key drivers of carbon emissions in Vietnam's electricity sector from 2002 to 2022 and investigates the evolving decoupling dynamics between economic growth and emissions. Employing the IPCC (2006) emission factor methodology for emissions estimation and the Tapio decoupling model to evaluate GDP-emissions elasticity, the analysis reveals a dramatic rise in emissions over the period, accelerating post-2010 amid 8-10% annual electricity demand growth. Coal's share in power generation escalated from 18% in 2005 to about 50% in 2020, fueling multiple-fold emission increases. The decoupling trajectory unfolds in three phases: expansive negative decoupling dominated 2001-2010, signaling carbon-intensive development; intermittent strong decoupling appeared in 2011-2015 despite coal's persistence; and sustained strong decoupling emerged in 2019-2022, driven by renewable energy surges and efficiency gains. These insights emphasize Vietnam's coal dependency while underscoring renewables' role in decoupling sustainability. Policy recommendations advocate expedited clean energy adoption, power mix restructuring, and reduced coal reliance to meet climate goals.
References
Matijašević, T., Antić, T., & Capuder, T. (2022). A systematic review of machine learning applications in the operation of smart distribution systems. Energy reports, 8, 12379-12407.
Zhao, E. D., Song, J. C., Chen, J. M., Liu, L. W., & Chen, M. S. (2022). Will auctioning promote the renewable energy generation in China?. Advances in Climate Change Research, 13(1), 107-117.
Oyebanji, M. O., & Kirikkaleli, D. (2023). Green technology, green electricity, and environmental sustainability in Western European countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(13), 38525-38534.
Chen, H., Zheng, Y., Zhou, K., Cheng, R., Zheng, X., Ma, Z., & Shi, L. (2023). Carbon emission efficiency evaluation of wastewater treatment plants: evidence from China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(31), 76606-76616.
Tang, Y., Ding, H., Shan, X., & Wang, X. (2023). Application of the novel three-stage DEA model to evaluate total-factor energy efficiency: A case study based on 30 provinces and 8 comprehensive economic zones of China. Results in Engineering, 20, 101417.
Fu, L., & Wang, C. (2022). Performance of the combination of decarbonisation policy instruments and implications for carbon neutrality in China. Advances in Climate Change Research, 13(6), 923-937.
Lefstad, L., Allesson, J., Busch, H., & Carton, W. (2024). Burying problems? Imaginaries of carbon capture and storage in Scandinavia. Energy Research & Social Science, 113, 103564.
Zhou, C., & Chen, X. (2023). Forecasting China's energy consumption and carbon emission based on multiple decomposition strategy. Energy Strategy Reviews, 49, 101160.
Liu, H., Liu, Q., He, R., Li, F., & Lu, L. (2024). Decomposition analysis and decoupling effects of factors driving carbon emissions produced by electricity generation. Energy Reports, 11, 2692-2703.
Abid, N., Wu, J., Ahmad, F., Draz, M. U., Chandio, A. A., & Xu, H. (2020). Incorporating environmental pollution and human development in the energy-growth nexus: a novel long run investigation for Pakistan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 5154.
Zhang, Y., & Pan, B. (2023). Shared responsibility of carbon emission for international trade based on carbon emission embodied between developing and developed countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(7), 19367-19379.
Environmental and Public Health, J. O. (2023). Retracted: Implicit Environmental Injustice in Global Trade: Based on the MRIO Model.
Nguyen, P. T. (2022). Carbon emissions versus value-added in export-driven countries: case of Vietnam. Journal of Economic Structures, 11(1), 12.
Feng, T. T., Gong, X. L., Guo, Y. H., Yang, Y. S., Pan, B. B., Li, S. P., & Dong, J. (2020). Electricity cooperation strategy between China and ASEAN countries under ‘The Belt and road’. Energy Strategy Reviews, 30, 100512.
Li, M., Peng, J., Lu, Z., & Zhu, P. (2023). Research progress on carbon sources and sinks of farmland ecosystems. Resources, Environment and Sustainability, 11, 100099.
Chen, F., Zhao, T., & Wang, D. (2022). Research on China cities’ total factor productivity of carbon emission: Based on decoupling effect. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2007.
Xiong, H., Wang, X., & Hu, X. (2023). Research on the duality of China’s marine fishery carbon emissions and its coordination with economic development. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1423.