Research on Colorectal Polyp Semantic Segmentation Based on E-UNet Network
Keywords:
Colorectal Polyp, Semantic Segmentation, Pyramidal Convolution, Soft Pooling, Improved CBAMAbstract
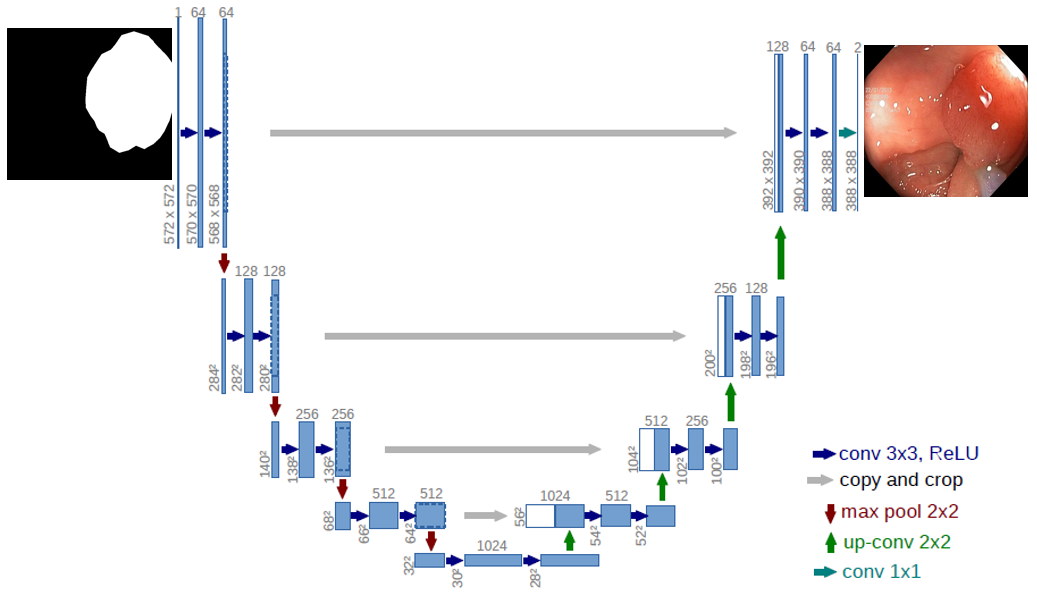
This study proposes an enhanced computer network named E-UNet, designed to improve the semantic segmentation capability for colorectal polyps. Addressing challenges in colorectal polyp images such as immense scale variations, blurry boundaries, and color similarity to the background, E-UNet makes key improvements based on the UNet architecture. First, Pyramidal Convolution (PyConv) is adopted to replace standard convolution, solving the problem of multi-scale feature extraction without increasing computational cost. Second, Soft Pooling is introduced to replace Max Pooling, reducing information loss during down-sampling and preserving more key low-amplitude signals such as blurry boundaries and subtle textures. Finally, an improved CBAM (I-CBAM) attention mechanism is designed. By processing channel and spatial attention in parallel and optimizing the MLP structure, it dynamically focuses on polyp morphology and key features, thereby overcoming issues such as the similarity between polyp and background colors. Experimental results on the authoritative public dataset Kvasir-SEG show that E-UNet outperforms mainstream methods such as UNet, UNet++, and Attention UNet across all evaluation metrics, achieving an mIoU of 87.5%, an mRecall of 91.9%, and an mPrecision of 93.1%. Ablation studies further verify the effectiveness of the I-CBAM, PyConv, and Soft Pooling modules, with the complete model achieving a 3.7% mIoU improvement compared to the baseline UNet.
References
Jafar, A., Abidin, Z. U., Naqvi, R. A., & Lee, S. W. (2024). Unmasking colorectal cancer: A high-performance semantic network for polyp and surgical instrument segmentation. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 138, 109292.
Manan, M. A., Feng, J., Yaqub, M., Ahmed, S., Imran, S. M. A., Chuhan, I. S., & Khan, H. A. (2024). Multi-scale and multi-path cascaded convolutional network for semantic segmentation of colorectal polyps. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 105, 341-359.
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., & Darrell, T. (2015). Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3431-3440).
Yu, F., & Koltun, V. (2015). Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.07122.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., & Brox, T. (2015, October). U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (pp. 234-241). Cham: Springer international publishing.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 770-778).
Paszke, A., Chaurasia, A., Kim, S., & Culurciello, E. (2016). Enet: A deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.02147.
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., & Cipolla, R. (2017). Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 39(12), 2481-2495.
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., & Jia, J. (2017). Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2881-2890).
Chen, L. C., Yang, Y., Wang, J., Xu, W., & Yuille, A. L. (2016). Attention to scale: Scale-aware semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3640-3649).
Chen, L. C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., & Adam, H. (2018). Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 801-818).
Lin, G., Milan, A., Shen, C., & Reid, I. (2017). Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1925-1934).
Duta, I. C., Liu, L., Zhu, F., & Shao, L. (2020). Pyramidal convolution: Rethinking convolutional neural networks for visual recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.11538.
Li, Z., Yang, S., & Zhao, Z. (2025, May). Oracle Bone Inscription Recognition Based on the S-MobileViT Network. In 2025 5th International Symposium on Computer Technology and Information Science (ISCTIS) (pp. 118-123). IEEE.
Stergiou, A., Poppe, R., & Kalliatakis, G. (2021). Refining activation downsampling with SoftPool. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 10357-10366).
Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 2018: 3-19.
Liu, K., Song, J., Zhao, Z., Liu, H., Qu, Z., & Wang, S. (2025, April). Research on the Recognition of Bamboo and Silk Scripts Based on the E-MobileViT Network. In Proceedings of the 2nd Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Education Digitalization and Computer Science International Conference (pp. 172-178).
Jha, D., Smedsrud, P. H., Riegler, M. A., Halvorsen, P., De Lange, T., Johansen, D., & Johansen, H. D. (2019, December). Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In International conference on multimedia modeling (pp. 451-462). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Zhou Z, Rahman Siddiquee M M, Tajbakhsh N, et al. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation[C]//International workshop on deep learning in medical image analysis. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 3-11.
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L. L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., ... & Rueckert, D. (2018). Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999.