Research on Teaching Reform of Natural Language Processing Courses in Application-Oriented Undergraduate Institutions
Keywords:
Natural Language Processing, Curriculum Reform, Large Language Models, Project-Based Teaching, Technology EvolutionAbstract
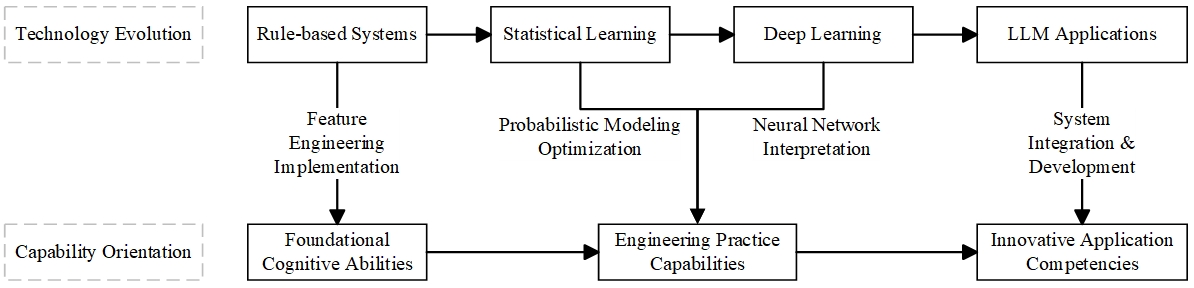
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence and big data technologies has led to a growing significance of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in undergraduate education, particularly within the context of application-oriented undergraduate institutions that integrate industry and education. There is an urgent need to revamp NLP curricula in higher education institutions, as current courses predominantly focus on theoretical knowledge, overlooking practical applications and failing to align with industry demands. In line with China's Emerging Engineering Education initiative, universities must enhance their AI-related curriculum to better address industrial needs. This study proposes a four-phase teaching framework ("rule-driven methods—statistical learning—deep learning—large model applications") tailored for application-oriented undergraduate institutions, with a focus on utilizing large pre-trained language models like BERT and ChatGPT as primary entry points. The curriculum integrates fundamental theories, practical experiments, and engineering skills development, encompassing essential tasks such as Chinese word segmentation, part-of-speech tagging, named entity recognition, text classification, and sentiment analysis. It incorporates state-of-the-art pre-training techniques and generative applications to ensure a comprehensive and systematic approach. Pedagogically, the framework advocates for project-based learning, case-driven methodologies, and comparative analysis of technological advancements. Experimental sessions are designed to accommodate varying levels of student proficiency and hierarchical computing requirements, incorporating modern strategies like online intelligent Q&A and flipped classrooms. Furthermore, the study outlines reform objectives including the development of generative applications, lightweight deployment experiments, and education on the security and ethics of large models. Continuous evaluation mechanisms are proposed to enhance students' overall literacy and practical skills in NLP applications.